ISSUE1371
Varenicline (Chantix), which has been associated with neuropsychiatric symptoms such as agitation, depressed mood, changes in behavior and suicidal ideation, appears to be the most effective drug available for treatment of tobacco dependence.1 Recently, the FDA warned that varenicline may also increase the risk of cardiovascular adverse events in patients with cardiovascular disease.2 This warning was based on the results of a 12-week randomized trial in 714 smokers with stable cardiovascular disease. The drug was effective in helping patients stop smoking; long-term quit rates (at 52 weeks) were 19% with varenicline and 7% with placebo.3 The results also included the following cardiovascular adverse events:
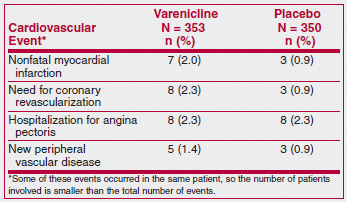
The authors of the study interpreted these results as providing reassurance that varenicline appears to be safe for use in smokers with stable cardiovascular disease. The FDA interpreted them as an association with a small increased risk of cardiovascular events if varenicline is used in patients with stable cardiovascular disease, and required the manufacturer to add this information to the labeling of the drug.
After the FDA's decision, a meta-analysis of 14 clinical trials in a total of 8216 patients with or without heart disease found that serious cardiovascular events occurred in 52 (1.06%) of 4908 patients treated with varenicline and in 27 (0.82%) of 3308 taking placebo. This difference was statistically significant.4
Until more data become available, the benefit of varenicline in helping patients stop smoking would appear to outweigh the risks of the drug.
